本文部分资料文件请前往https://www.jinyuttsrz.top/index.php/archives/89/下载
本文部分资源来自【黑马程序员】,【菜鸟教程】 学习更多内容:前往菜鸟教程
numpy是一个python中做科学计算的基础库,重在数值计算,也是大部分python科学计算库的基础库,多用于在大型,多维数组上执行数值计算。
NumPy 安装
pip3 install numpy 或使用第三方镜像站下载
pip3 install numpy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
安装验证
import numpy as np
print(np.__version__)
若输出版本号则安装成功,如:2.2.6
创建数组(矩阵)
使用numpy生成数组,得到ndarray的类型
import numpy as np
t1 = np.array([1,2,3])
print(t1)
print(type(t1))
输出内容:
[1 2 3]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
使用range,arange创建数组
t2 = np.array(range(10))
print(t2)
print(type(t2))
t3 = np.arange(4,10,2) #用法与range一致,用于快速生成一堆数组
print(t3)
print(type(t3))
输出内容:
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
[4 6 8]
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>Numpy中的数据类型
print(t3.dtype)
输出内容:
int64
通过dtype可以指定相关的数据类型:
t4 = np.array(range(1,10),dtype=float)
print(t4)
print(t4.dtype)
输出内容:
[1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.]
float64
numpy中的bool类型:
t5 = np.array([1,1,0],dtype=bool)
print(t5)
print(t5.dtype)
输出内容:
[ True True False]
bool
photo 加载中

使用astype调整数据类型
t6 = t4.astype("int8")
print(t6)
print(t6.dtype)
输出内容:
[1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9]
int8
Numpy中的小数
import random
t7 = np.array([random.random() for _ in range(10)])
print(t7)
print(t7.dtype)
t8 = np.round(t7, 2)
print(t8)
print(t8.dtype)
输出内容:
[0.44545863 0.00578244 0.15234127 0.57536716 0.42175181 0.73858965
0.40943437 0.81574412 0.2461211 0.94405275]
float64
[0.45 0.01 0.15 0.58 0.42 0.74 0.41 0.82 0.25 0.94]
float64
数组的形状
import numpy as np
t11 = np.arange(12)
print(t11)
print(t11.shape)
输出内容:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11])
(12,)
#当这个数组为一维数组时,将仅输出一个数:组内数据数量
.
t12 = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
print(t12)
print(t12.shape)
输出内容:
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
(2, 3)
当数组为二维数组时,将输出两个数:行的数量,列内数据数数
.
t13 = np.array([[[1,2,12],[3,4,11]],[[5,6,10],[7,8,9]]])
print(t13)
print(t13.shape)
输出内容:
array([[[ 1, 2, 12],
[ 3, 4, 11]],
[[ 5, 6, 10],
[ 7, 8, 9]]])
(2, 2, 3)
三维列表输出:块数量,行数量,列内数据数量
数组形状修改:reshape(存在返回值,不会直接对原数据进行修改,需要接收)
print(t12.reshape([3,2]))
输出内容:
array([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]])
当修改为无法生成的形状时,将报ValueError错误
生成数组时可以使用此方法修改数组的形状:
t14 = np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
print(t14)
输出内容:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
使用flatten可以快速展开数组为一维数组
print(t14.flatten())
输出内容:
array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23])
数组的计算(广播原则)
Print(t14+2)
#其他计算同理,特殊点:可以/0
输出内容:
array([[[ 2, 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13]],
[[14, 15, 16, 17],
[18, 19, 20, 21],
[22, 23, 24, 25]]])
.
t14/0 #当对一个数组进行除0
输出内容:
Warning (from warnings module):
RuntimeWarning: divide by zero encountered in divide
Warning (from warnings module):
RuntimeWarning: invalid value encountered in divide
array([[[nan, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, inf]],
[[inf, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, inf],
[inf, inf, inf, inf]]])
Inf代表无穷大 nan代表不是一个数字not a number
数组之间可以进行相加等处理
t14 = np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4))
t15 = np.arange(100,124).reshape((2,3,4))
print(t14+15)
print(t14*t15)
输出内容:
array([[[100, 102, 104, 106],
[108, 110, 112, 114],
[116, 118, 120, 122]],
[[124, 126, 128, 130],
[132, 134, 136, 138],
[140, 142, 144, 146]]])
array([[[ 0, 101, 204, 309],
[ 416, 525, 636, 749],
[ 864, 981, 1100, 1221]],
[[1344, 1469, 1596, 1725],
[1856, 1989, 2124, 2261],
[2400, 2541, 2684, 2829]]])当数组形状满足一个维度一致时也可进行操作,不一致时会返回ValueError错误
t16=np.arange(0,4)
t17=np.arange(0,3).reshape(3,1)
print(t16)
print(t17)
print(t15*t16)
print(t15*t17)
输出内容:
array([0, 1, 2, 3])
array([[0],
[1],
[2]])
array([[[ 0, 101, 204, 309],
[ 0, 105, 212, 321],
[ 0, 109, 220, 333]],
[[ 0, 113, 228, 345],
[ 0, 117, 236, 357],
[ 0, 121, 244, 369]]])
array([[[ 0, 0, 0, 0],
[104, 105, 106, 107],
[216, 218, 220, 222]],
[[ 0, 0, 0, 0],
[116, 117, 118, 119],
[240, 242, 244, 246]]])
Numpy中的倒置
Transpose用于倒置数据,在对角线方向交换数据,为了能够更方便处理数据
t18 = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
print(t18)
print(t18.transpose)方法同:print(t18.T)
输出内容:
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]])
array([[ 0, 4, 8],
[ 1, 5, 9],
[ 2, 6, 10],
[ 3, 7, 11]])
轴
photo 加载中

photo 加载中
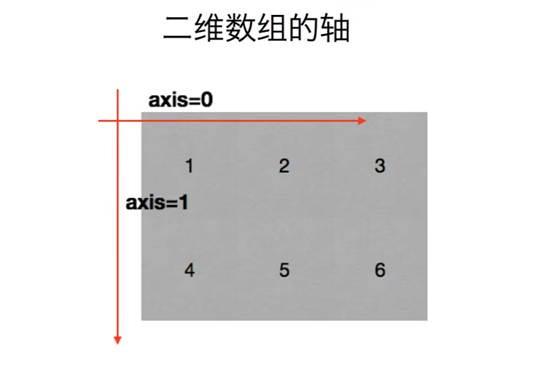
photo 加载中
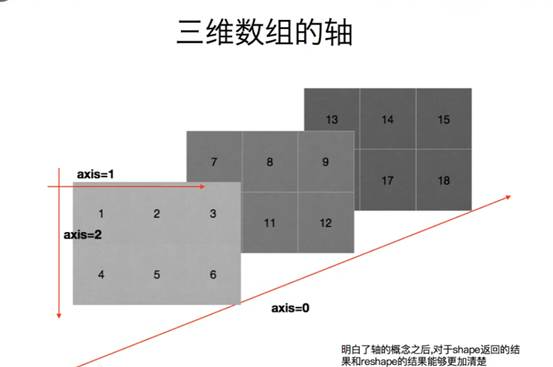
photo 加载中
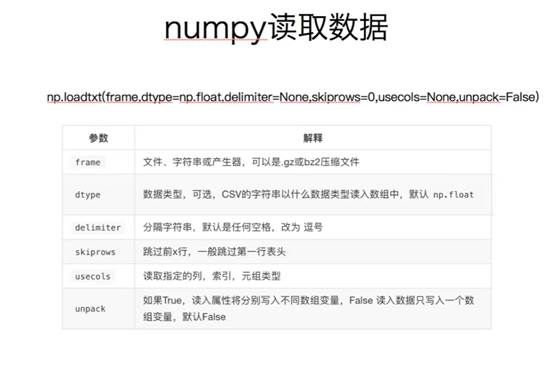
Numpy数据读取
完成对数据的读取:读取文件
US_video_data_numbers.csv
GB_video_data_numbers.csv
us_path = "./US_video_data_numbers.csv"
uk_path = "./GB_video_data_numbers.csv"
TUK = np.loadtxt(uk_path, delimiter=',', dtype="int")
#可用unpack=True通过对角线旋转,行列对倒
TUS = np.loadtxt(us_path, delimiter=',', dtype="int")
print(TUK)
print(TUS)
输出内容:
photo 加载中
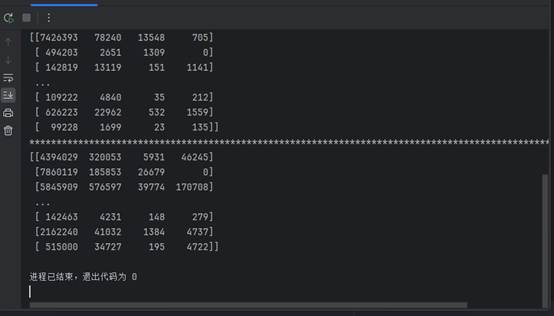
Numpy索引和切片
取单行:
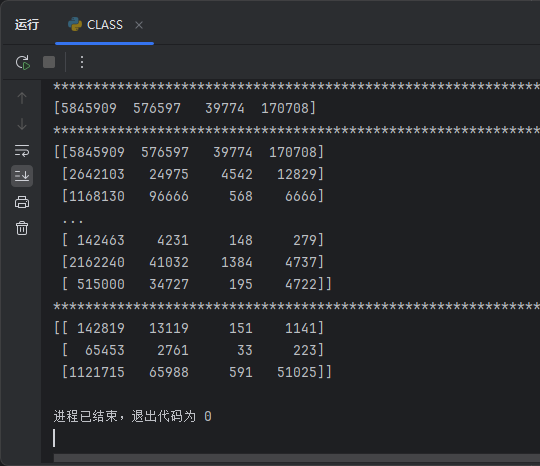
print(TUS[2])
取连续多行:
print(TUS[2:])
取不连续的多行:
print(TUS[[2,8,10]])
输出结果:
photo 加载中
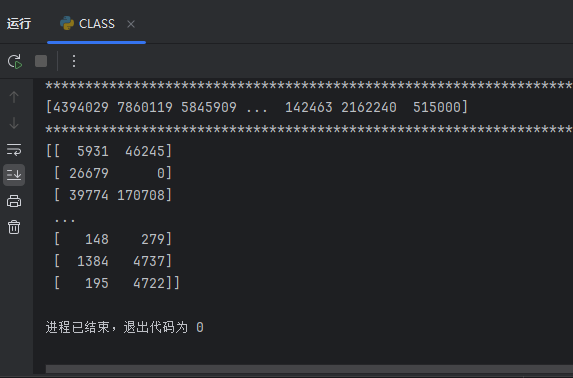
取列:
print(TUS[:,0])
取连续的多列:
print(TUS[:,2:])
输出结果:
photo 加载中
取行列,第三行第四列:
t = TUS[2,3]
print(t)
print(type(t))
输出结果:
170708
<class 'numpy.int64'>
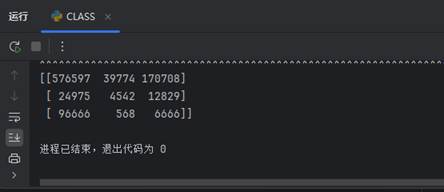
取多行多列:第三行到第五行,第二列到第四列的结果:
t = TUS[2:5,1:4]
print(t)
输出结果:
photo 加载中
Numpy中数值的修改
t = np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
t[t<5] = 1满足t<5则赋值1(布尔判断)
photo 加载中

Numpy中的三元运算符
np.where(t<=3,100,300)
np.where(条件,满足则修改为,不满足则修改为)
array([[100, 100, 100, 100],
[100, 300, 300, 300],
[300, 300, 300, 300]])
Numpy中的nan和inf
photo 加载中
t[2,2] = np.nan
需要浮点数据才能赋值nan,否侧会报ValueError 异常
使用astype转换数据类型
t = t.astype(float)
t[2,2] = np.nan
输出结果:
photo 加载中

photo 加载中

Numpy中常用的统计函数
photo 加载中
Numpy中的clip裁切
photo 加载中
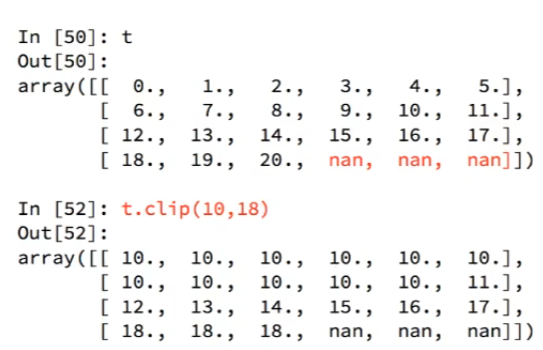
t.clip(小于此数的数字替换为此数,大于此数的数替换为此数,nan不操作)
Nampy中填充nan的方法代码
import numpy as np
def fill_ndarray(t1):
for i in range(t1.shape[1]):
temp = t1[:, i] #当前的列
# count_nonzero方法可以统计当前数据中nan的个数
nan_nu = np.count_nonzero(temp != temp)
if nan_nu != 0: #说明有nan
#取不为nan的数据,取法为:nan互不相等
temp_not = temp[temp == temp] #当前列不为nan的数组
# 选中nan位置,赋值其为均值
temp[np.isnan(temp)] = temp_not.mean()
#使用mean方法,进行填充
return t1
if __name__ == '__main__':
t1 = np.arange(12).reshape(3, 4).astype("float")
t1[1, 2:] = np.nan
#随机取两个数据改为nan进行模拟
print(t1)
print("*"*100)
t1 = fill_ndarray(t1)
print(t1)

comment 评论区
star_outline 咱快来抢个沙发吧!